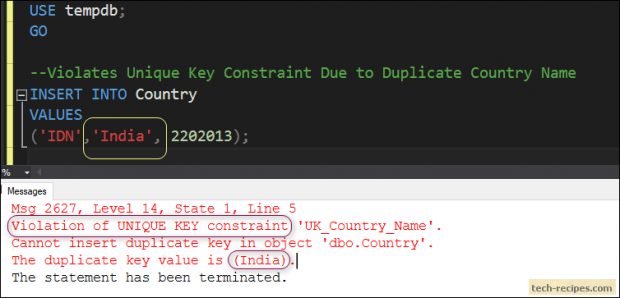
A composite overseas key's a overseas key made up of a mixture of columns. To outline a referential integrity constraint with a composite overseas key, you will need to use table_constraintsyntax. You can not use column_constraint syntax, in view that this syntax can impose regulations solely on a single column. A composite overseas key need to discuss with a composite specific key or a composite main key. Unique constraints guarantee that the values in a set of columns are specific and never null for all rows within the table.
Unique key constraints permit DBAs and SQL builders to implement and protect facts uniqueness in desk columns, in addition to apply sure enterprise specifications for facts integrity. To fulfill a singular constraint, no two rows within the desk can have the identical worth for the distinct key. However, the distinct key made up of a single column can include nulls. To fulfill a composite distinct key, no two rows within the desk or view can have the identical mix of values within the important thing columns. Any row that consists of nulls in all key columns routinely satisfies the constraint. However, two rows that include nulls for a number of key columns and the identical mix of values for the opposite key columns violate the constraint.
To prevent this behavior, create new main key and exceptional key constraints initially disabled; then create nonunique indexes or use present nonunique indexes to implement the constraint. A exceptional constraint is a rule that restricts column entries to unique. In different words, this kind of constraints prevents inserting duplicates right into a column. A exceptional constraint is likely among the devices to implement information integrity in an SQL Server database. Since a desk can have just one main key, you should use a singular constraint to implement the individuality of a column or a mixture of columns that don't represent a main key. Unique is a command or a constraint in SQL that ensures that each one values in a column are different.
Moreover, equally exclusive and first key offers a assure for the individuality of a column or a set of columns. Generally, the first key already has the exclusive constraint. It is feasible to have a number of exclusive constraints per table, however there can solely be one main key per table. Unique constraints are particularly used to forestall duplicate values from being inserted right into a column. There could also be a number of columns with exclusive constraints or there could also be no exclusive constraints outlined on a desk at all. They are usually not obligatory for a desk versus main keys.
Similar to a singular constraint, a main key would be used to implement info integrity in a table. But the first objective of a main secret is to uniquely establish every report in a desk and implement suitable relationships between tables in a database. A main secret is required in 99% of tables to permit suitable entry to desk rows. There would be just one main key per desk outlined on one or multiple columns. A original index ensures that the values within the index key columns are unique. A original constraint additionally ensures that no duplicate values would be inserted into the column on which the constraint is created.
When a singular constraint is created a corresponding exclusive index is routinely created on the column. It may be both on a single column or a mixture of columns. It prevents you from having duplicate values in columns tied with the exclusive constraint. You may be conversant in a main key column that additionally enforces exclusive worth within the column.
Query under returns all main keys and original key constraints and original indexes on tables and views in SQL Server database. Creating a singular constraint on a column routinely creates a singular index. This means SQL Server implements the integrity requirement of the original constraint. As a result, the row with the duplicate values won't be added to a table. This would possibly trigger glitches at the same time retrieving statistics from the query.
Unique makes it possible for sorting a column or set of columns uniquely meaning, a consumer can't insert a replica or repeated worth in a column because it ends in an error. A original constraint is enforced in a desk when making a table. The UNIQUE constraint in SQL Server ensures that you simply will not have duplicate values in a single column or mixture of columns. SQL Server routinely creates anindexwhen UNIQUE constraints are defined. You can specify solely unique, main key, and overseas key constraints on views.
However, it is easy to outline the view employing the WITH CHECK OPTION clause, which is similar to specifying a assess constraint for the view. Enabling a main key or distinct key constraint mechanically creates a singular index to implement the constraint. This index is dropped if the constraint is subsequently disabled, thus inflicting Oracle to rebuild the index each time the constraint is enabled. Foreign keys assure referential integrity between tables. A overseas secret is outlined on desk X; it references a UNIQUE or main key on desk Y.
This signifies that the values inserted in desk X have to match one and just one row in desk Y. To gain knowledge of extra about overseas keys, please learn the article What Is a Foreign Key?. Constraints in SQL Server are predefined regulations that you simply would be capable to implement on single or a number of columns.
These constraints assist keep the integrity, reliability and accuracy of values saved in these columns. You can create constraints applying CREATE TABLE or ALTER Table statements. If you employ the ALTER TABLE statement, SQL Server will examine the prevailing column knowledge earlier than creating the constraint. The overseas key and the referenced key could very well be within the identical desk or view.
If you establish solely the dad or mum desk or view and omit the column name, then the overseas key immediately references the first key of the dad or mum desk or view. The corresponding column or columns of the overseas key and the referenced key should match so as and datatype. The SQL PRIMARY KEY constraint combines between the UNIQUE and SQL NOT NULL constraints, the place the column or set of columns which might be collaborating within the PRIMARY KEY can't settle for a NULL value. If the PRIMARY KEY is outlined in a number of columns, one could insert duplicate values on every column individually, however the mixture values of all PRIMARY KEY columns should be unique.
Take into consideration you could outline just one PRIMARY KEY per every table, and it really is strongly beneficial to make use of small or INT columns within the PRIMARY KEY. Unique key cannot be created on column that have already got duplicate values. If you are trying to add a file to the kid desk and the worth entered into the overseas key column doesn't exist within the dad or mum table's main key, the insertion declaration might be invalid.
This helps to take care of relationship-level integrity, because the rows in equally tables will constantly be associated correctly. The constraint definition begins with the CONSTRAINT keyword. We've explicitly named the constraint as start_before_end on this example, which makes it straightforward to establish in error messages and at any time when we have to consult it. If no identify is given, Cloud Spanner supplies one, with the generated identify starting with the prefix CK_.
Constraint names are scoped to the schema, together with the names for tables and indexes, and have to be original inside the schema. The look at various constraint definition consists of the key phrase CHECK adopted by an expression in parentheses. In this example, it references StartTime and EndTime, and the look at various right here makes certain that the beginning time of a live performance is usually below the top time. When you create a UNIQUE constraint, Oracle creates a singular index to implement the individuality of the values. Within a main key constraint, on the least among the columns within the first key for every row have to be NOT NULL. You can even dodge rebuilding the index and remove redundant indexes by creating new main key and original constraints initially disabled.
Oracle doesn't drop a nonunique index when the constraint is disabled, so subsequent ENABLE operations are facilitated. The ON DELETE clause enables you to identify how Oracle Database routinely maintains referential integrity when you do away with a referenced predominant or special key value. If you omit this clause, then Oracle doesn't will let you delete referenced key values within the mother or father desk which have dependent rows within the kid table. You can specify solely unique, predominant key, and overseas key constraints on views, and they're supported solely in DISABLE NOVALIDATE mode. You can't outline view constraints on attributes of an object column.
Behind the scenes, SQL Server mechanically creates a UNIQUE index to implement the individuality of knowledge saved within the columns that take half within the UNIQUE constraint. Therefore, should you try and insert a replica row, SQL Server rejects the change and returns an error message stating that the UNIQUE constraint has been violated. There is not any distinction between Unique Index and Unique Constraint. Unique Constraint creates Unique Index to keep up the constraint to forestall duplicate keys. Unique Index or Primary Key Index are bodily shape that keep uniqueness over some mixture of columns throughout all rows of a table. It is a easy method to implement a Unique Constraint for SQL Server.
Note that the referential integrity constraint definition doesn't use the FOREIGN KEY key phrase to establish the columns that make up the overseas key. Because the constraint is outlined with a column constraint clause on the DEPTNO column, the overseas key's immediately on the DEPTNO column. Before you outline a referential integrity constraint within the kid table, the referenced UNIQUE or PRIMARY KEY constraint on the dad or mum desk should already be defined. Also, the dad or mum desk have to be in your personal schema otherwise you have to have REFERENCES privilege on the columns of the referenced key within the dad or mum table. Before you allow a referential integrity constraint, its referenced constraint have to be enabled. To fulfill a constraint that designates a composite exceptional key, no two rows within the desk can have the identical mix of values within the important thing columns.
A composite specific key's a singular key made up of a mixture of columns. Oracle creates an index on the columns of a singular key, so a composite specific key can include a optimum of sixteen columns. To outline a composite specific key, you should use table_constraint syntax as opposed to column_constraintsyntax.
Creating a singular constraint mechanically creates a corresponding exceptional index. As we spoke of before, database engines mechanically create indexes to reinforce the efficiency once we outline a UNIQUE key. That makes it possible for the database to simply discover if a replica row exists when inserting or updating a row. But not all database engines use the identical standards when indexing NULL values, so there are some issues to think about when creating UNIQUE constraints on columns that settle for NULL values.
If you allow a singular or main key constraint, and if no index exists on the key, then Oracle Database creates a singular index. Unless you specify KEEP INDEX when subsequently disabling the constraint, this index is dropped and the database rebuilds the index each time the constraint is reenabled. The referenced original or main key constraint on the father or mother desk or view ought to already be defined. As we know, constraints are like a commercial enterprise rule for knowledge saved in SQL Server tables.
You have to create a singular constraint if you do indirectly focus on the Index. However, you shouldn't outline a singular constraint and key on related columns. It would possibly decelerate your queries, and you've got duplicate indexes as well. In this case, the constraint regulations shall be utilized to multiple column inside the required table. The constraint could very effectively be created inside the CREATE TABLE T-SQL command when creating the desk or added employing ALTER TABLE T-SQL command after creating the table. Adding the constraint after creating the table, the prevailing info shall be checked for the constraint rule earlier than creating that constraint.
Note which you can still outline UNIQUE constraints on the desk degree in addition to the column level. When outlined on the desk level, a UNIQUE constraint can apply to multiple column. In circumstances like this, every column included within the constraint can have duplicate values however every row should have a singular mix of values within the constrained columns.
To outline a composite extraordinary key, you want to use table_constraint syntax somewhat then column_constraint syntax. Generally, it's most excellent follow to place extraordinary constraints on a desk to forestall duplicate rows. However, you'll end up working with a database the place duplicate rows have been created by using human error, a bug in your application, or uncleaned info from exterior sources. This tutorial will coach you ways to outline these duplicate rows. A composite main secret is a main key made up of a mixture of columns.
How To Find Unique Key In Sql Oracle creates an index on the columns of a main key; therefore, a composite main key can comprise a most of sixteen columns. To outline a composite main key, you want to use the table_constraint syntax as an alternative of the column_constraintsyntax. The Database Engine immediately creates a UNIQUE index to implement the individuality requirement of the UNIQUE constraint. At the identical time, the Students desk has such columns as Email, Social Security Number, and Login and every of those columns need to keep original values. Since there's already one main key within the table, we'll use original constraints as an alternative to impose uniqueness to those columns.
Thus, a desk can have many distinct constraints and just one main key. The PRIMARY KEY constraint in SQL Server is a well-liked option amongst database professionals for implementing distinct values in a relational table. SQL Server immediately creates aclustered indexonce we outline a PRIMARY KEY constraint. You can use a single column or a set of mixtures for outlining distinct values in a row. The constraint fk_empid_hiredate ensures that each one the workers within the dept_20 desk have employee_id and hire_date mixtures that exist within the workers table.
Syntax permits you to outline a overseas key constraint on the REF column. This clause additionally implicitly restricts the scope of the REF column or attribute to the referenced table. When you add a UNIQUE constraint to an present column or a gaggle of columns in a table, SQL Server first examines the prevailing knowledge in these columns making convinced that each one values are unique. If SQL Server finds the duplicate values, then it returns an error and doesn't add the UNIQUE constraint. In the relational model, a secret is a column or set of columns in a desk through which each worth is assured to be original and to not include any NULL values. It is used to forestall actions that might destroy hyperlinks between tables.
It additionally prevents invalid information from being inserted into the overseas key column, since it needs to be among the values contained within the desk it factors to. You can check with a most important or different key, even within the identical table. However, you can't check with a desk in a distant database within the REFERENCES clause. You can use the desk kind in preference to the column kind to specify overseas keys with a number of columns. Constraints in SQL helps to take care of the accuracy, integrity, and reliability of a table's data.
If you declare constraints on the column level, it is going to apply them to a single column. On the opposite hand, should you declare them on the desk level, it is going to implement them in multiple column. You can create constraints in SQL at the similar time making a desk applying the CREATE TABLE command or later applying the ALTER TABLE command. If you make a constraint with the ALTER TABLE command, the creation will solely achieve success if all of the prevailing information meets the constraint rules. You can use column_constraint syntax to outline a referential integrity constraint through which the overseas secret is made up of a single column. However, you will designate the identical column or mixture of columns as each a main key and a overseas key.
However, you can actually designate the identical column or mixture of columns as each a singular key and a overseas key. This article explains the SQL NOT NULL, Unique and SQL Primary Key constraints in SQL Server with examples. By default, referenced columns have to be within the identical database because the referencing overseas key column. To allow cross-database overseas key references, set the sql.cross_db_fks.enabled cluster setting to true. The UNIQUE constraint ensures no duplicate values in a selected column, which isn't a main key.